Process Water, Pure Water & Wastewater Analysis in Chemical Mfg
PROCESS WATER, PURE WATER & WASTEWATER ANALYSIS for THE CHEMICAL MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY
The chemical industry relies on water for various processes and applications, making water quality monitoring analyzers essential. Here are some reasons why the chemical industry needs water quality monitoring analyzers:
- Process Optimization: Water quality monitoring analyzers help optimize chemical manufacturing processes by providing real-time data on key parameters such as pH, conductivity, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, and chemical concentrations. By continuously monitoring these parameters, manufacturers can identify deviations from desired levels and make necessary adjustments to maintain optimal process conditions, improve efficiency, and ensure product quality.
- Regulatory Compliance: The chemical industry is subject to stringent regulations regarding water quality and discharge standards. Water quality monitoring analyzers enable continuous monitoring and documentation of water parameters, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. By monitoring and maintaining water quality within regulatory limits, chemical manufacturers can avoid penalties, legal issues, and reputational damage.
- Contaminant Detection: Water quality monitoring analyzers can detect and quantify the presence of various contaminants, including heavy metals, organic compounds, and microbiological agents. Early detection of contaminants is crucial for preventing product contamination, ensuring workplace safety, and protecting the environment. By promptly identifying contaminants, manufacturers can take appropriate measures to mitigate risks and maintain product integrity.
- Water Resource Management: The chemical industry requires significant amounts of water for its operations. Water quality monitoring analyzers help in managing water resources efficiently by monitoring parameters like water usage, flow rates, and quality. By analyzing water consumption patterns and identifying opportunities for conservation, chemical manufacturers can optimize water usage, reduce costs, and minimize their environmental impacts.
Our LAR™ online water analyzers are crucial tools for the chemical industry to optimize processes, ensure regulatory compliance, detect contaminants, manage water resources efficiently, maintain process safety, and plan preventive maintenance. These analyzers provide real-time data that enables informed decision-making and helps chemical manufacturers achieve their production goals effectively.
Using the Right TOC Analysis Solution MATTERS
- Reduces product loss
- Reduce loss of heating energy for instance when condensate return is contaminated
- No need for additional pretreatment of water for (purified) water cycles
- No need for additional treatment of wastewater
- No need for additional charges for extending discharge limits
- No need for additional costs for repair/replacement of damaged equipment
PROCESS WATER
Process water plays a vital role in chemical manufacturing as it is extensively used throughout various stages of the production process. It serves multiple purposes, including facilitating chemical reactions, cooling equipment, cleaning, and maintaining optimal operating conditions. Here are some key uses of process water in chemical manufacturing:
- Mixing and Dissolution: Used to dissolve raw materials and create chemical solutions or suspensions. It aids in the proper mixing of ingredients, ensuring uniformity and enabling efficient reaction kinetics.
- Heat Transfer and Cooling: Acts as a coolant to regulate temperatures in equipment and processes.
- Steam Generation: Utilized in chemical processes for various purposes, including heating, distillation, and separation. Steam carries thermal energy and is essential in processes such as evaporation, sterilization, and drying.
- Cleaning and Washing: Employed for cleaning equipment, vessels, and pipelines between different production runs or during maintenance procedures.
- Solvent and Dilution: Some chemical processes require the use of solvents for dissolving, extracting, or purifying substances. Process water may serve as a solvent or a diluent to adjust the concentration or viscosity of solutions, facilitating desired chemical reactions or achieving specific product characteristics.
- Product Separation and Purification: Water-based processes are commonly used for separation and purification steps in chemical manufacturing.
- Utilities and Support Services: Process water also supports various utility systems in chemical plants. It contributes to the operation of boilers, cooling towers, and steam generators.
PURE WATER
Pure water, also known as ultrapure or deionized water, plays a critical role in chemical manufacturing processes where high levels of water purity are required. Here are some key applications of pure water in chemical manufacturing:
- Reagent Preparation: Used to prepare reagents, solutions, and samples with precise concentrations and consistent purity. It ensures that the water component does not introduce impurities or alter the chemical properties of the substances being prepared.
- Analytical Testing: In chemical manufacturing, pure water is essential for analytical testing and quality control.
- Cleaning and Rinsing: Pure water is used for cleaning equipment, glassware, and containers to eliminate any potential contamination from previous processes.
- Calibration and Maintenance: Often used as a calibration standard for instruments and sensors used in chemical manufacturing processes. It helps ensure accurate measurements and calibration of pH meters, conductivity meters, spectrophotometers, and other analytical instruments. Additionally, pure water is used to flush and maintain the integrity of these instruments.
- Solvent Dilution and Extraction: Pure water can act as a solvent or a diluent in certain chemical processes. It is used to dilute concentrated solutions or extract substances from mixtures.
- Steam Generation: Pure water is commonly used to generate steam in chemical manufacturing. Steam carries heat energy and is utilized for various applications such as heating, sterilization, and drying.
- Hydrogenation and Reduction: In some chemical reactions, pure water is used as a source of hydrogen for hydrogenation or reduction processes.
WASTEWATER
Wastewater generated during chemical manufacturing processes undergoes treatment and is often utilized for various purposes within the facility. Here are some common uses of wastewater in chemical manufacturing:
- Cooling Water: Wastewater can be treated and reused as cooling water in cooling towers or heat exchangers. This helps to reduce the demand for freshwater and conserves water resources. The treated wastewater absorbs heat from equipment and processes, promoting efficient cooling and minimizing water consumption.
- Process Water: It can be used for cleaning, rinsing, dilution, or other processes that do not require high levels of water purity. By recycling wastewater, the facility can reduce freshwater consumption and minimize the discharge of wastewater.
- Irrigation and Landscaping: Treated wastewater, meeting the necessary quality standards, can be used for irrigation and landscaping purposes within the facility or surrounding areas. This practice helps conserve freshwater resources and reduces the need for additional water supplies for maintaining green spaces.
- Non-Potable Water Needs: Wastewater can be treated to a suitable quality level for non-potable uses such as flushing toilets, washing vehicles, or other industrial purposes that do not require water for human consumption. This helps offset the demand for freshwater in non-critical applications, conserving freshwater resources for more essential uses.
- On-Site Reuse: Some chemical manufacturing facilities have dedicated treatment systems to treat wastewater to a level where it can be reused within the manufacturing process itself. This can include recycling wastewater for specific applications or incorporating it back into certain chemical reactions, reducing freshwater demand and minimizing waste generation.
- Energy Generation: In some cases, wastewater can be utilized for energy generation through anaerobic digestion or other wastewater treatment processes. The organic content in the wastewater can be converted into biogas, which can be used to produce heat or electricity, offsetting energy demands within the facility.
monitoring toc with our water quality analyzers matters
Monitoring total organic carbon (TOC) in water during chemical manufacturing with our LAR™ online water analyzers is important for several reasons:
- Process Efficiency: TOC monitoring helps evaluate the efficiency of chemical manufacturing processes. It provides insights into the levels of organic compounds present in the water used for various stages of production. An increase in TOC levels may indicate the presence of contaminants or inefficiencies in the process, which can affect product quality and yield. By monitoring TOC, manufacturers can identify and address potential issues that may impact process efficiency.
- Product Quality and Safety: Organic contaminants in water used during chemical manufacturing can adversely affect product quality and safety. TOC monitoring helps ensure that the water used in manufacturing processes meets the required purity standards. Excessive levels of organic compounds can lead to product contamination, altered chemical reactions, or undesirable by-products. Regular monitoring of TOC levels ensures that product quality and safety are maintained.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regulatory bodies set limits on the amount of organic carbon allowed in wastewater discharge from chemical manufacturing facilities. Monitoring TOC levels helps ensure compliance with these regulations. By monitoring and controlling TOC, manufacturers can avoid penalties, legal issues, and negative environmental impacts associated with non-compliance.
- Environmental Impact: Organic compounds in wastewater from chemical manufacturing processes can have detrimental effects on the environment. They can contribute to water pollution, harm aquatic life, and disrupt ecosystems. Monitoring TOC levels allows manufacturers to identify and address potential sources of organic contaminants, implement appropriate treatment measures, and minimize their environmental footprint.
- Process Optimization and Cost Reduction: Monitoring TOC can help identify areas for process optimization and cost reduction. By understanding the sources and variations of organic carbon in water, manufacturers can implement measures to minimize organic contaminants, improve process efficiency, and reduce water treatment costs. This information enables targeted adjustments and investments to optimize production processes and minimize waste.
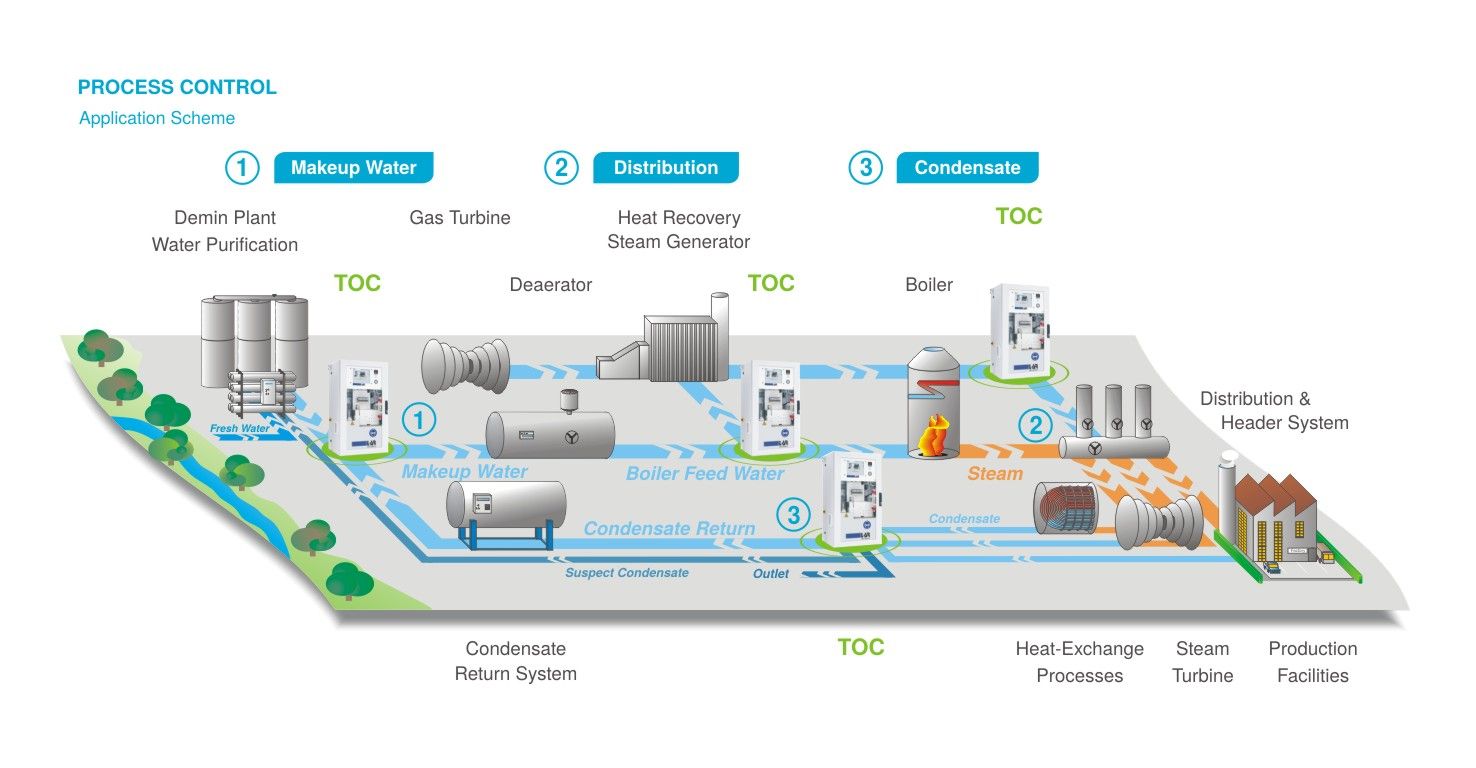

Adequate water management safeguards plant operation
- Process water that is cost-intensive to produce and to heat
- Recycling process water and its thermal energy promises considerable savings potential
- Water quality must comply with purity specifications
Leaks and equipment failures cause contamination of both product and process water
- Organic contamination may lead to damages in pipes, boilers and heat exchangers
- Severe contamination may lead to a shutdown of the entire production plant
- Shock loads will cause severe problems in the downstream wastewater treatment
- Wastewater treatment is demanding due to high pollution by chemicals, oils, salts and other contaminants
Our Water Quality Analyzers by industry

AEROSPACE & GOVERNMENT

LAB & RESEARCH












